

Hearing function in congenital anomalies of the ear is very difficult to improve since patients may present with associated deformities that cannot be properly repaired.

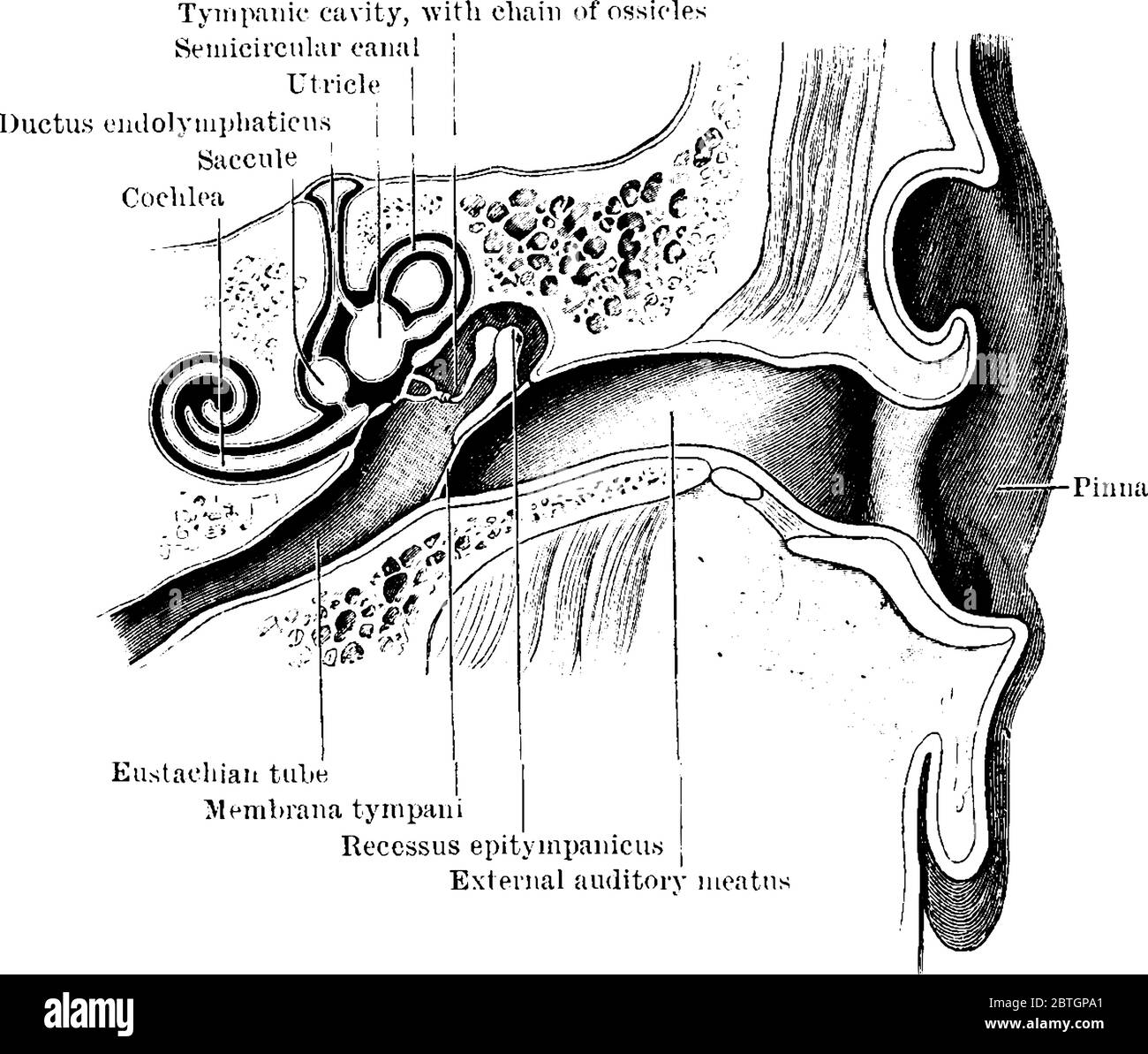
with complication of the boil by BTE lymphadenitis, differential diagnosis with acute mastoiditis should be performed Diagnosis in this direction is difficult when combining the furuncle of the external auditory canal with acute or chronic suppurative inflammation of the middle ear at the same time they are based on the nature of swelling in the behind-eye area: with mastoiditis, puffiness and infiltration are located in the posterior region of the posterior region in the projection of the mastoid cave with smoothing of the bovine furrow, with the furuncle of the external auditory meatus with behind-the-ear adenitis in the posteriorly retroaureic region while maintaining the relief of the bovine furrow.The absence of the external auditory canal may be repaired in order to reinstate the esthetic harmony of the auricle.adenitis or parotitis, in which formation of fistulas in the external auditory can occur with these diseases pressing on the area in front of the tragus increases the discharge from the external auditory canal.acute purulent otitis media take into account the otoscopic picture, localization and nature of pain, the nature of purulent discharge and the degree of hearing loss.acute diffuse external otitis, which is characterized by the spread of the process outside the external ear canal into the auricle and into the bovine furrow Diagnosis is difficult for eczema complicated by the furuncle of the external auditory canal.eczema of the external auditory canal, for which severe pain, and mostly itching, is not characteristic.The diagnosis is made on the basis of the clinical signs described above.ĭifferential diagnosis is carried out in the following directions: With several furuncles, as a rule, there is a complete overlap of the external auditory canal, the clinical course is aggravated, there is a pastost in the behind-the-ear with bulging of the auricle, which can simulate mastoiditis.ĭiagnosis of furuncle of external auditory canal The furuncle can open itself, in this case yellowish-greenish pus is secreted, after removal of which a small hole in the form of a crater can be found on top of the infiltrate. At the top of the swelling, a yellowish "hood" is formed, under which an accumulation of pus is found. When otoscopy at the beginning of the disease, a limited reddish swelling is found at the entrance to the external auditory meatus, which gradually increases for several hours and partially overlaps the external auditory canal. When obstructing the external auditory canal, an inflammatory infiltrate causes conductive hearing loss of the ear with lateralization of tissue sound in the diseased ear. At night, the pain intensifies, becomes unbearable, because of which the patient is completely deprived of sleep. The latter circumstance causes the patient to refuse food. The pain in the ear grows quickly and is accompanied by irradiation into the corresponding half of the head, sharply increasing with chewing movements. At the beginning of the disease in the external auditory canal, the patient feels a strong itching, turning into pain. Therefore, with the development of an inflammatory infiltrate, there is a significant pressure on the pain receptors causing intolerable pain, which in intensity often exceeds the pain syndrome in acute non-perforative inflammation of the middle ear. The peculiarity of the clinical picture of the furuncle of the external auditory canal, in contrast to its localization on the open surface of the skin, is that it arises and develops in a confined space with abundant innervation of the nerves of pain sensitivity.
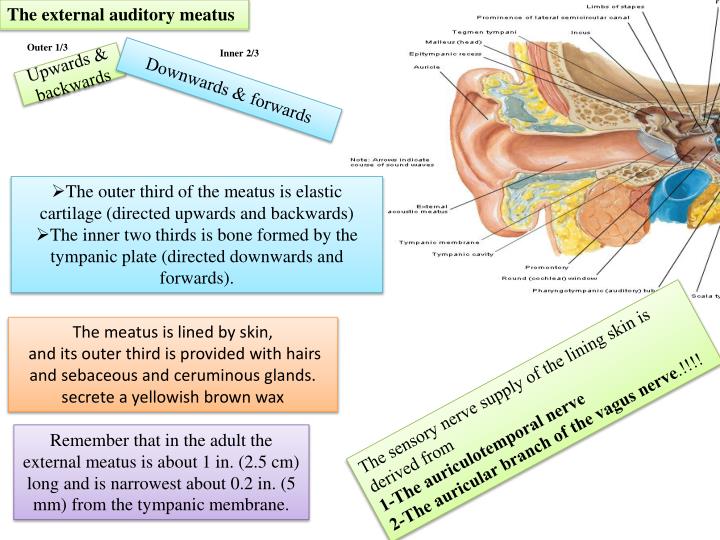
Symptoms of furuncle of external auditory canal


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
